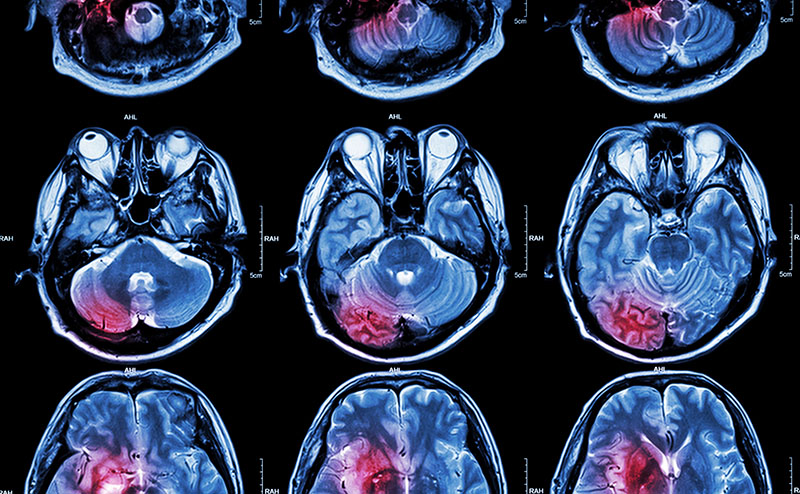
A head injury may seem innocuous at first—a little slip and a bump to the head—but it could be far more dangerous.
If a person loses consciousness after a head injury, then the person has had a “concussion,” which may be serious because it means there has been a temporary loss in brain function. Some people with concussions do not lose consciousness, and brain injuries can occur without a loss of consciousness.
Severe head injuries can involve bruising, fracture, swelling, internal bleeding or a blood clot. Seek emergency care if you notice any of these signs of severe head injury:
- Headaches that worsen, despite over-the-counter pain medications.
- Weakness, numbness or decreased coordination.
- Repeated vomiting.
- Loss of consciousness for more than one minute.
- Person is unconscious or cannot be awakened.
- Unequal pupil sizes — one pupil (the black part in the middle of the eye) is larger than the other.
- Convulsions or seizures.
- Slurred speech.
- Increased confusion or agitation.
You do not need to prevent a person with a head injury from sleeping as a safeguard against going into a coma; this concept is a myth. If the person has neck pain, try to prevent any movement of the neck.
Click here for more information about child head injuries.
 American College of Emergency Physicians
American College of Emergency Physicians